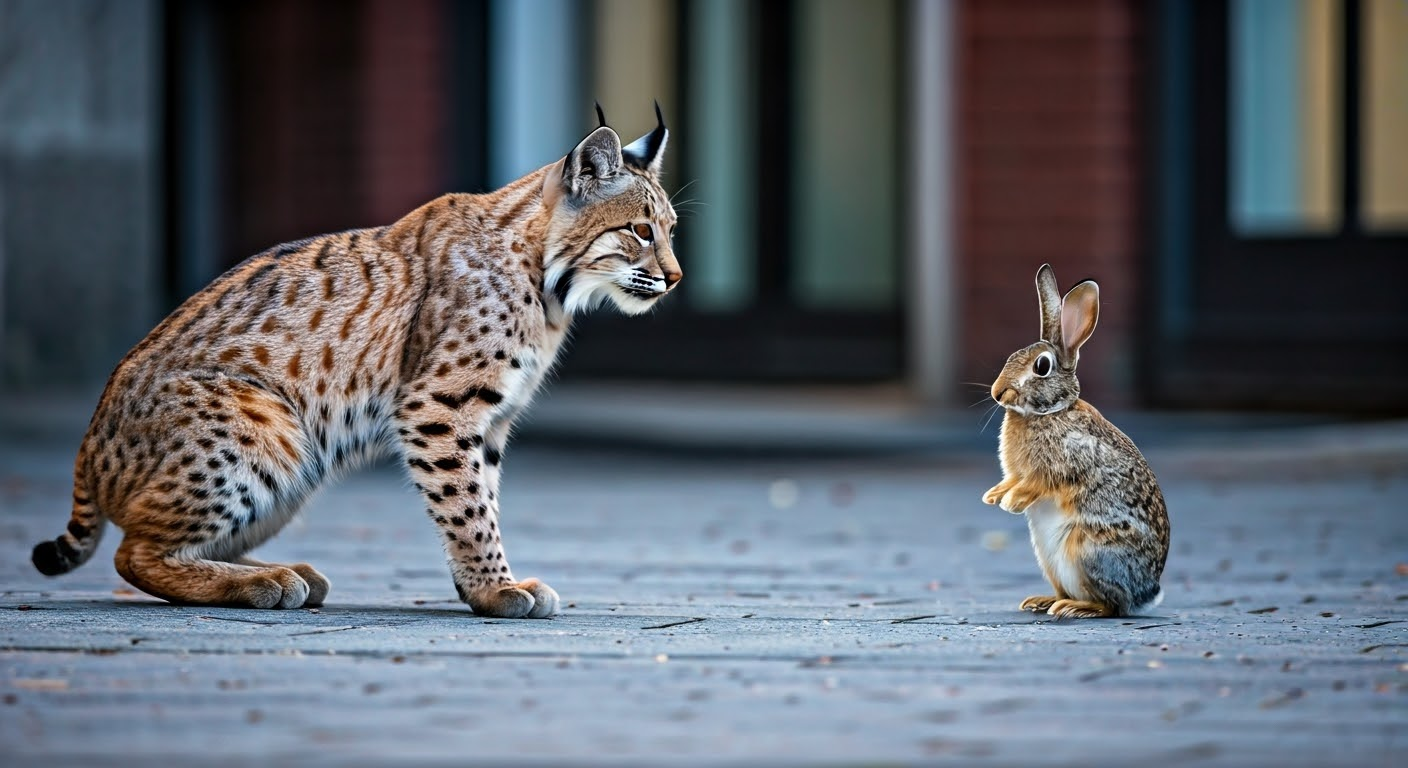
Urban wildlife has many challenges as cities grow and take away their homes. Animals like the bobcat and the black-tailed jackrabbit, which is called Lepus californicus, change how they act to adjust to city life. They adapt to the number of people around them and the new spaces they discover. Also, coyotes, known as Canis latrans, are another danger. When we look at how bobcats and their prey, like rabbits, survive in cities, we can learn more about how they live in tough situations.
Key Highlights
- Cities influence how animals, such as bobcats and rabbits, behave and move around.
- Understanding how they adapt is important. It helps them survive close to us and keeps people safe.
- Seasons and human actions can change these animals’ daily schedules.
- Bobcats are great hunters, but they may change their hunting methods in cities.
- Watching their behavior can help us manage wildlife more effectively in urban areas.
- Knowing these changes can create a safer space for both people and wildlife.
Understanding Urban Wildlife: Bobcats and Rabbits

- Rabbits are a key food source for animals like bobcats.
- They can change their diet easily based on available plants.
- You can often see them in parks, city greens, and home gardens.
- This ability helps them find food, even when they are by themselves.
- That’s why urban areas are great habitats for rabbits.
Bobcats need easy food to eat. We should study how rabbits and bobcats interact in cities. This information can help us create better plans for managing wildlife. By watching their actions and paths, we can understand how urban life affects wildlife numbers.
The rise of urban wildlife habitats
Urbanization has been good for some animals, such as bobcats, and their prey. This occurs for several reasons:
- Lots of food: Cities have a lot of food for the animals that predators hunt. Many people grow gardens, and this attracts predators like bobcats looking for an easy meal.
- Less competition: In cities, people can scare away larger predators like cougars and bears. This means smaller predators, like bobcats, can have a better chance to survive.
- Adaptability: Bobcats and their prey are good at adjusting to life in the city. They learn how to cross streets and find shelter in buildings. These animals find ways to live and do well in their new homes.
Adaptations of bobcats and rabbits to urban environments
Urban wildlife faces many problems. Animals need to adapt to live in these areas. For prey species, such as rabbits, being alert is very important. They often change how they look for food. These changes help them stay away from predators. They also help them find food near humans. This way, their chances of survival get better.
Bobcats are changing their hunting ways in cities. They now hide in plants and buildings to get closer to their prey. They eat different types of food, like rodents and birds. This change helps them survive and thrive in the city.
The way predators change their behavior and how prey species keep safe in cities is very interesting. Knowing about these changes is important. It helps us protect and manage prey animals better in urban areas.
Analyzing Behavior and Movement Patterns
Studying how bobcats and rabbits behave in the city helps us understand their lives. When we watch what they do each day, we can see how their behavior changes with the seasons. We notice patterns in what they do. These patterns are affected by people, the weather, and what resources are available in the city.
This information is key for conservation. It helps people care for habitats better. It can also lower problems between people and wildlife. When we know how animals move in the city, it gives us useful insight to manage wildlife in urban areas.
Seasonal and daily activity cycles of bobcats and rabbits
The predator and prey cycle can also occur in cities. Many factors in the environment can affect how this cycle works. Rabbits usually come out in the morning and evening. Their behavior changes depending on the seasons. When it is warm or if there is little rain, they are active for longer. This helps them find food during the cooler times of the day.
Bobcats hunt when the sun sets. They pick this time because their prey, such as rabbits, are out and active. This helps them be good hunters. However, in the city, they might act differently. Bright lights and crowds can change their usual behavior.
These changes show how animals adapt to life in cities. When we watch what they do, we can spot possible issues. This knowledge can help us discover better ways to share space in our city.
Impact of urbanization on their natural behaviors
Urbanization changes the homes of animals and increases human activity. This makes life tough for wildlife. Animals are adjusting their behavior to cope with these changes. Prey species are more likely to encounter predators in these altered areas. As a result, they are becoming more aware of their surroundings. They are also changing how they find food to stay safe.
In cities, animals can find food quite easily. They eat leftover trash and plants from gardens. This changes their regular diet and gives them more food than usual. Although this might seem good, it can be bad for their health. It can also disturb the balance of nature.
- Bobcats can be affected by living close to cities.
- When they feel secure around people, they become bolder.
- This could lead to more encounters with humans and pets.
- To improve the situation for both people and wildlife, we should learn about these behavior changes.
- Understanding this can help reduce issues in city areas.
Interaction Between Bobcats and Rabbits in City Settings

Predators and prey interact differently in cities. Bobcats and rabbits have found ways to live close to people. Their actions change to fit city life. For example, buildings and streetlights can change how they hunt and where they hide.
These new situations help us understand how animals live in different places. When we watch what they do, we can learn how to reduce conflicts. This way, people and animals can happily coexist in our cities.
Predatory behavior of bobcats towards rabbits in urban areas
Urbanization affects how bobcats hunt. In areas where people live, there are more Lepus californicus and other prey such as rodents and birds. This extra food makes it simpler for bobcats to find a meal. They have a greater chance of doing well because food is easier to find.
In some city places, there are not many big animals like Canis latrans, which are coyotes. Because of this, bobcats have to hunt more. With fewer animals to compete with for food, bobcats can get better at hunting. This might change the number of prey animals in that area.
Seeing how bobcats hunt in cities helps us understand how they change to fit their surroundings. It also shows how different parts of the city are linked. This information is important for making smart decisions about managing wildlife in urban areas.
Survival strategies of rabbits amidst urban predators
Rabbits play a key role as prey for bobcats. In cities, they face several dangers. Even so, rabbits are tough and can adapt to their environment, which helps them survive. They have great hearing and a strong sense of smell. These skills help them spot threats and find safer places in thick plants or burrows.
Rabbits breed quickly. This helps keep their numbers up, even when there are predators around. They are herbivores, so they eat plants. Rabbits enjoy grasses, shrubs, and vegetables from gardens. This provides them with a good food supply, especially in city areas.
Animals find it hard to live in cities. Both predators and prey face challenges to survive in urban settings. If we pay attention, we can observe how wild animals act when people are close by.
Conclusion
In cities, bobcats and rabbits show us how animals adjust to life with people. To get along well, we need to learn about their actions and behaviors. As cities expand, we should care about their health and keep both animals and humans safe. By observing how they eat, live, and react to sounds, we can discover better ways to support them. Keeping their populations steady reminds us how important balance is in nature, even in city areas. We must value and protect the wildlife that shares our environment as they adapt.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do urban environments affect the diet of bobcats and rabbits?
Urban areas can change what bobcats and rabbits eat. Bobcats mostly go for easier prey. They often hunt rodents and birds that are near people. Meanwhile, rabbits tend to eat more plants from gardens and lawns. This changes what these herbivores usually eat.
Can bobcats and rabbits coexist peacefully in urban settings?
Coexisting with bobcats and their prey, like rabbits, is possible in cities if we act wisely. We should teach people how to share their space with these animals. This involves keeping items that might attract bobcats safe. We also need to help natural habitats grow.
What measures can be taken to protect urban wildlife while ensuring human safety?
- We need to find new ways to protect animals and keep people safe in cities.
- We should build wildlife paths to help animals move safely.
- It is key to reduce light pollution so animals feel less bothered.
- Teaching people about wildlife living in cities is important.
- Helping everyone understand what to do when they spot animals can stop issues.
How does urban noise pollution impact bobcats and rabbits?
Noise in cities can make it hard for animals to communicate and find food. This noise affects how they hunt and behave as predators or prey. Loud sounds can stress both prey, like rabbits, and their hunters, such as bobcats. This stress can lower their chances of survival and caring for their young.
Are there successful examples of bobcat and rabbit population management in urban areas?
Cities in Mexico have discovered smart ways to take care of themselves.
|
City |
Management Strategy |
Target Species |
|
San Diego, California |
Habitat restoration and connectivity projects |
Bobcats |
|
Mexico City, Mexico |
Public education and community-based habitat management |
Rabbits (various herbivores) |
Hi, I’m Sondip,
I’m a writer who loves to help people solve their problems. I write about small animals like mice and other small animals and even pests.

